02 | Language and Machines
How machines think? #
The impetus behind creating artificial intelligence (AI) can be traced back to humanity’s enduring fascination with replicating its own cognitive abilities in artificial entities. This fascination is rooted in ancient myths and legends where master craftsmen endowed inanimate objects with intelligence or consciousness, exemplified by figures like Talos, a bronze giant in Greek mythology, and the Golem of medieval legends, which were believed to perform tasks or provide protection through imbued intelligence. Over centuries, this fascination evolved into philosophical and scientific pursuits to mechanize human thought, initially through the formal reasoning methods developed by philosophers like Aristotle and later by inventors and thinkers such as Leibniz and Descartes, who envisioned reasoning as a systematic process akin to mathematical computation.
This was writing by an AI of course.
Brief timeline of GenAI #
- 1956: Introduction of Artificial Intelligence as a science;
- 1958: Frank Rosenblatt proposed the scheme of a device that simulates the process in the human brain - perceptron, the world’s first neural network;
- 1964: Creation of one of the first functioning generative AI - ELIZA chatbot
- 1982: RNN is created, which takes prior information into account and generates sentences;
- 1997: A type of RNN with a more complex architecture called LSTM is developed, which allows efficient processing of long sequences of data and identifies patterns;
- 2013: Creation of a generative model called variational autoencoders (VAE);
- 2014: Creation of GANs, which were a breakthrough in generative AI as they were among the first to generate high-quality images. GAN has received more attention, also due to the higher degree of complexity of the theoretical basis of VAE compared to the more straightforward concept underlying GAN;
- 2015: Introduction of diffusion models that function by incorporating noise into the existing training data and then reversing the process to restore the data;
- 2017: Deep learning architecture referred to as transformer was proposed;
- 2018: Groundbreaking Generative pre-trained transformers (GPT), a type of large language model, was introduced by OpenAI;
- 2021: AI platform DALL-E intended for generating and editing unique artworks and photorealistic images was launched;
- 2022: Open source Stable Diffusion and proprietary Midjourney AI image-generating tools were introduced;
- 2023: GPT-4 was released in March 2023, capable of generating longer texts up to 25000 words.
Neural Networks #
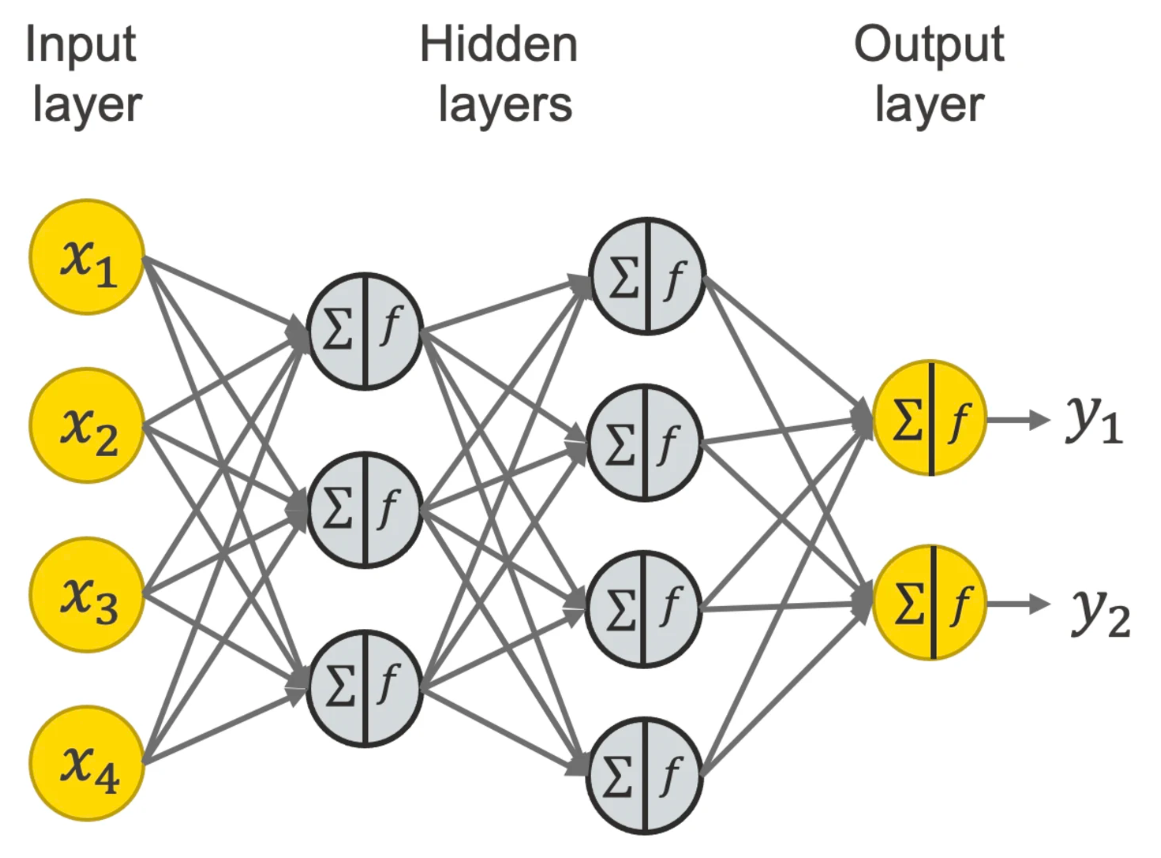
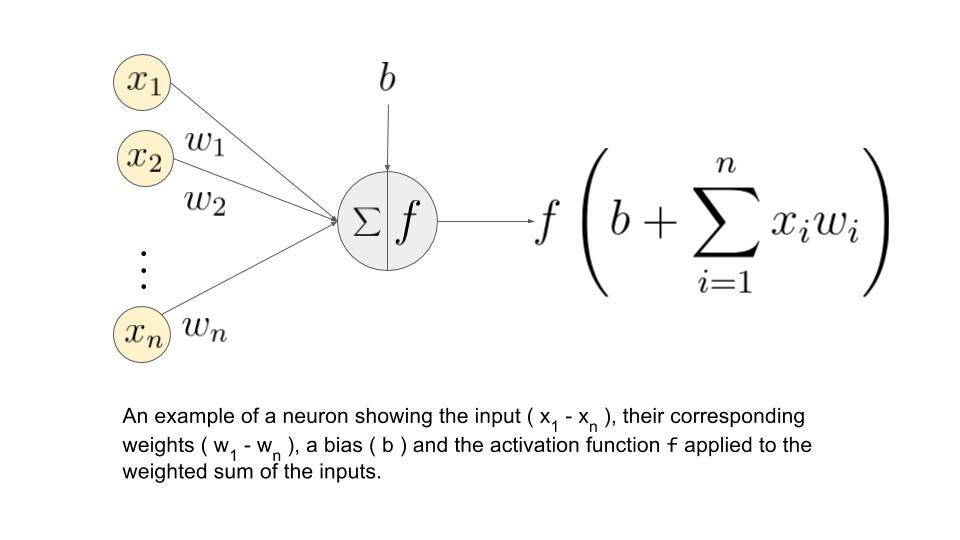
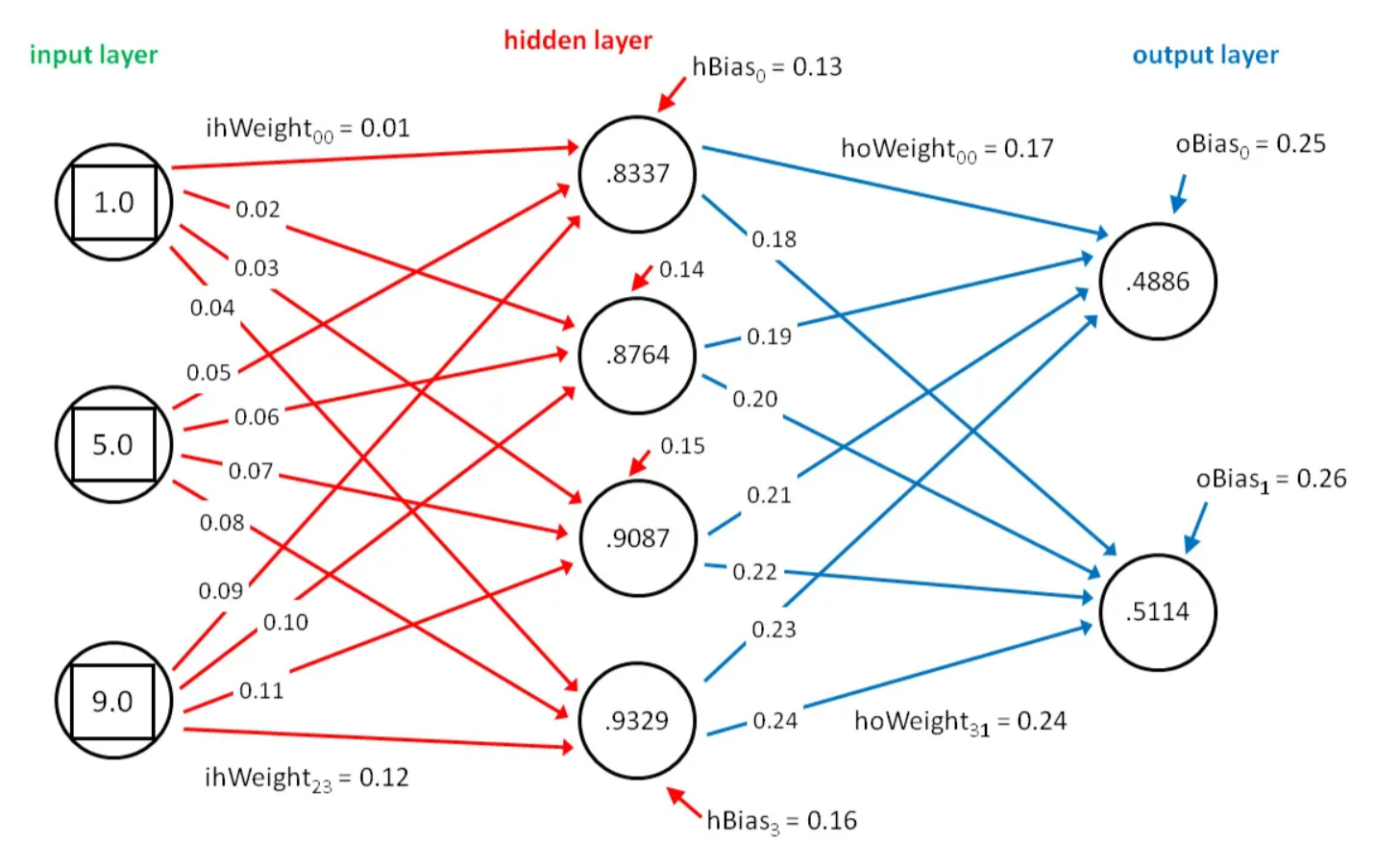
Neural networks are computational models inspired by the human brain’s structure and function, designed to recognize patterns by processing input data through layers of interconnected nodes, or neurons. Each neuron receives inputs, processes them using a mathematical function, and passes the output to subsequent neurons. The connections between neurons have weights that adjust as the network learns from data during a training phase, allowing it to make increasingly accurate predictions or decisions based on input data. The typical neural network architecture includes an input layer, one or more hidden layers where computation and transformation occur, and an output layer that delivers the final result, such as a classification or prediction.
This approach differs significantly from other computational paradigms like brute force coding, where explicit rules and steps must be defined for every possible scenario. Brute force methods simply try all possibilities to find a solution, which can be computationally expensive and impractical for complex problems. In contrast, neural networks learn to solve problems by generalizing from examples, without needing explicit programming for each new situation. This allows them to adapt to new, unseen data based on the learned patterns, making them particularly useful for tasks such as image and speech recognition, where the variability and complexity of the data make traditional approaches cumbersome and inefficient. Neural networks, therefore, offer a more flexible and scalable solution in environments where dynamic learning and adaptability are crucial.
This is Ai too, but a bit better
Transformers #
Transformers are a type of neural network architecture introduced in the paper “Attention is All You Need” by Vaswani et al. in 2017. They are designed primarily to handle sequential data, such as natural language, for tasks like translation and text summarization. Unlike traditional models that process data sequentially (like recurrent neural networks), transformers use a mechanism called self-attention to process all parts of the input data simultaneously. This allows them to capture complex relationships between input and output data efficiently and to scale better to large datasets.
The same problem that happens to RNNs generally, is that when sentences are too long LSTMs still don’t do too well. The reason for that is that the probability of keeping the context from a word that is far away from the current word being processed decreases exponentially with the distance from it.
The architecture of a transformer consists of an encoder that processes the input data and a decoder that generates the output. Each of these components is made up of layers that include attention mechanisms, which help the model to focus on different parts of the input for making decisions, and fully connected layers for transformation.
GPTs #
GPTs (Generative Pre-trained Transformers) operate using a transformer-based architecture optimized for natural language understanding and generation. They are initially pre-trained on vast amounts of text data to learn a wide range of language patterns and nuances. This pre-training involves predicting the next word in a sentence given the previous words (autoregressive training). Once pre-trained, GPTs can be fine-tuned with specific instructions or tasks, adapting their general capabilities to more specialized applications.
They process input text through multiple layers of self-attention mechanisms, which allow the model to weigh the relevance of all other words in the input for generating each subsequent word, thereby creating coherent and contextually appropriate text outputs. This design enables GPTs to perform a variety of language tasks, often with little to no task-specific training data beyond the initial pre-training phase.
LLMs #
Large Language Models (LLMs) are advanced machine learning models designed to understand and generate human-like text by processing vast amounts of written language. These models use deep learning techniques, typically based on the transformer architecture, to predict and generate text based on the patterns they learn during their training. LLMs are characterized by their massive size, often consisting of billions of parameters, which enable them to capture complex linguistic structures, nuances, and contexts. They are versatile in their applications, capable of performing a wide range of tasks such as translation, summarization, question answering, and creative writing, often with a high degree of proficiency. The capabilities of LLMs to handle diverse and complex tasks with little specific instruction make them powerful tools in the field of natural language processing and artificial intelligence.
Some of the most popular LLMs are:
Dimistifying AI #
Its all math, for now.
Even the most human-like interactions generated by AI are the result of mathematical functions and computations that process input data and produce outputs based on learned data patterns. Thus, while AI might seem mysterious or even like magic at first glance, every decision, prediction, and action it takes is rooted in mathematical calculations, making it a powerful but ultimately comprehensible tool.
But can they eventually think? #
The question of whether AI can achieve consciousness or self-awareness is a complex and philosophical one that has been debated for decades. While AI systems can exhibit impressive capabilities in understanding and generating human-like text, images, and other forms of data, they do not possess consciousness or self-awareness in the same way humans do. AI operates based on predefined algorithms, data patterns, and mathematical computations, without subjective experiences, emotions, or self-reflection. The ability of AI to generate human-like responses is a result of its training on vast amounts of data and its capacity to mimic patterns and behaviors, rather than true consciousness or self-awareness.
Relevant Links #
- What are neural networks
- 3B1B What are neural networks
- The mathematics of neural networks
- What are graph neural networks?
- Attention is all you need
- What are transformers
- What are GPTs
- How GPTs work
- What are LLMs
- What are large language models
- ChatGPT has a chatbot finally achieved self-awareness
- Did ChatGPT just become self-aware
- I convinced the chatbot Google Bard that it is a conscious and sentient entity
- On the machine condition and its creative expression
- Turin Test
- Artificial consciousness: what is it and what are the issues